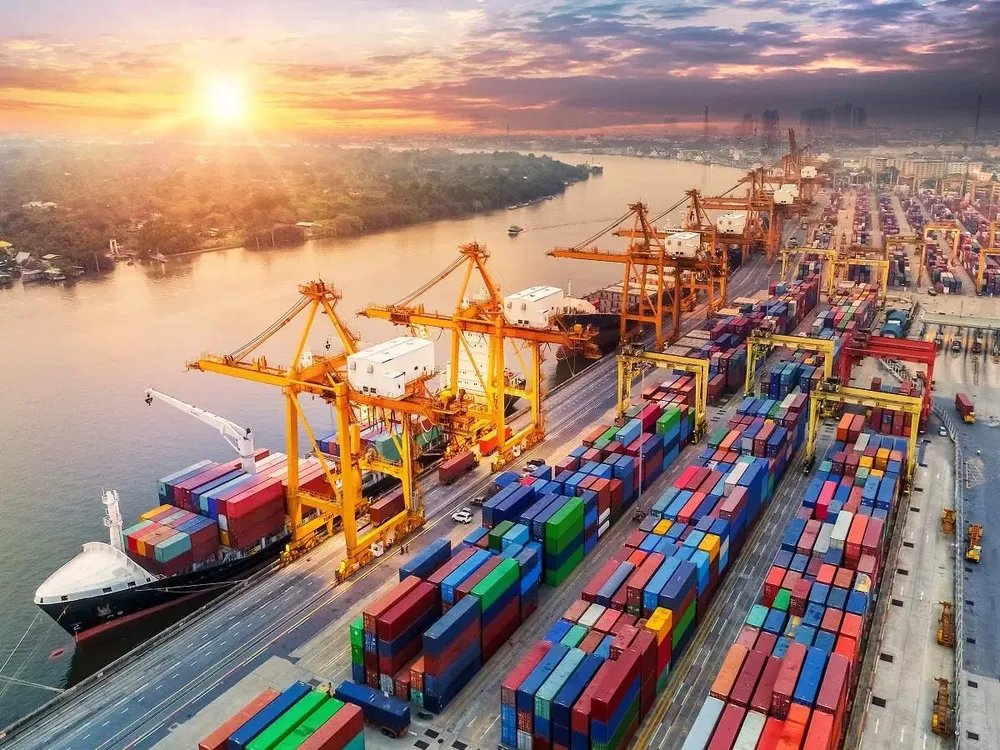
The textile and garment industry saw a turnover of USD 44 bln, while the seafood industry exceeded their target and brought in USD 11 bln. Nonetheless, many challenges still remain and 2023 is forecast to be a very difficult year for all exports.
Scenario for garments
At a conference to summarize the results of the garment industry in 2022, Mr. Vũ Đức Giang, Chairman of the Vietnam Textile and Apparel Association (Vitas), said that this year the textile industry has experienced many ups and downs, but still brought in an export turnover of USD 44 bln, up by 8.8% compared to 2021. In this, the US export market brought in more than USD 18 bln, South Korea USD 4.2 bln, and Japan USD 3.9 bln.
Looking back at 2022, businesses all agree that there were two clear periods. In the first six months of the year there was an exciting atmosphere when the orders increased sharply, especially during the first quarter. In the second quarter, growth started to become slower but still remained positive. However, in the last six months of the year, the decline was evident, partly due to the strong increase in purchasing power in the first and second quarters, but more importantly due to the rising inflation in many countries and lower consumer purchasing power.
However, in 2023 the garment industry offers two growth scenarios. The positive scenario is that the garment industry can reach USD 47 bln or USD 48 bln, and the less positive scenario is that the whole industry will reach only USD 45 bln or USD 46 bln. Behind these two scenarios are many worries for businesses when entering into 2023. Mr. Lê Tiến Trường, Chairman of Board of Directors of Vietnam Textile and Garment Group, said the latest survey results of Mckinsey on product clusters see growth in 2023, in which textiles and apparel and footwear are in the group with very low demand resilience compared to other industries.
Specifically in 2023, the garment industry will face the challenge of lack of orders and customers prolonging payment time. As per established practice, in the fourth quarter of the previous year, enterprises received applications for the first and second quarters of the following year. However, the situation of lack of orders in the first months of next year is happening in many enterprises.
Another concern that is also that the processing price of Vietnamese products is currently higher than that of many competing countries, because the local currencies of these countries has fallen sharply against the US dollar. In 2022, the Vietnamese dong fell about 5%, while the Bangladeshi taka fell 15%, the yuan fell 10%, the Indian rupee fell 7.8%, and the Pakistani rupee fell 25%. This makes the processing price of Vietnamese products 10% to 30% higher.
In addition to the immediate challenges, the garment industry is posing many long-term challenges in terms of growth rate, investment in green technology and green production. Mr. Lê Tiến Trường said that currently the advantages of Vietnam's textile and garments compared to other countries are not many, even if compared with Bangladesh in terms of access to technology and green production. According to an assessment, if Vietnam wants to maintain the 3rd position in garment exports in the world, it must accelerate pace in 2023, 2024 and 2025, which will not be easy.
Seafood industry worried
By the end of November, the seafood industry had reached a target of USD 10 bln and was expected to bring in USD 11 bln for the whole year, up 25% over the previous year, the highest in the industry's export history. In this, shrimp exports were expected to reach USD 4.3 bln, pangasius USD 2.5 bln, seafood USD 3.2 bln, and tuna USD 1 bln. In general, aquatic products have a double-digit growth of 18% to 77%.
In particular, the US market for the first time achieved a seafood turnover of over USD 2 bln and the UK became the 7th largest market of Vietnamese seafood. On the world seafood export map, Vietnam currently ranks 3rd, after China and Norway, and accounts for 7% market share in the world market.
Mr. Trương Đình Hòe, General Secretary of the Vietnam Association of Seafood Exporters and Producers (VASEP), said that Vietnam is proactive in raw materials and production, and businesses are flexible and persistent with market consumer trends. In addition, the growth of the seafood industry this year is sudden, and it is impossible to exclude the price increase in the first months of the year due to the strong increase in demand for seafood products in some markets after the Covid-19 pandemic.
Ms. Lệ Hằng, Director of Communications at VASEP, said that in December, seafood exports may fall further, and the decline will last until 2023. Inflation heavily affects import markets, causing demand and purchase in the first quarter of next year to almost stagnate. Ms. Lệ Hằng shared that many seafood enterprises said that orders dropped sharply, including demand for the next quarter, not only for high-priced items such as black tiger shrimp, large-sized white leg shrimp, and high-class seafoods such as squid, octopus, tuna, but also moderately priced products such as small shrimp, pangasius, small sea fish, and fish cakes.
The market in the first months of 2023 will also face many difficulties. Currently, many seafood enterprises are struggling with loans and interest rates to maintain raw material and production activities. At a recent conference in Can Tho, Mr. Lê Văn Quang, Chairman of the Minh Phu Seafood Corporation, said that the biggest concern of enterprises today is how to have around VND 200 bln to buy raw shrimp and pay salaries to staff. If they do not buy raw shrimp with the current decline in shrimp prices, farmers will not be able to fill their ponds.
The concern about capital of enterprises seems to be removed when the bank disbursed at the end of November, but the interest rate was still too high, making businesses afraid to borrow. This is a common situation for most businesses today.