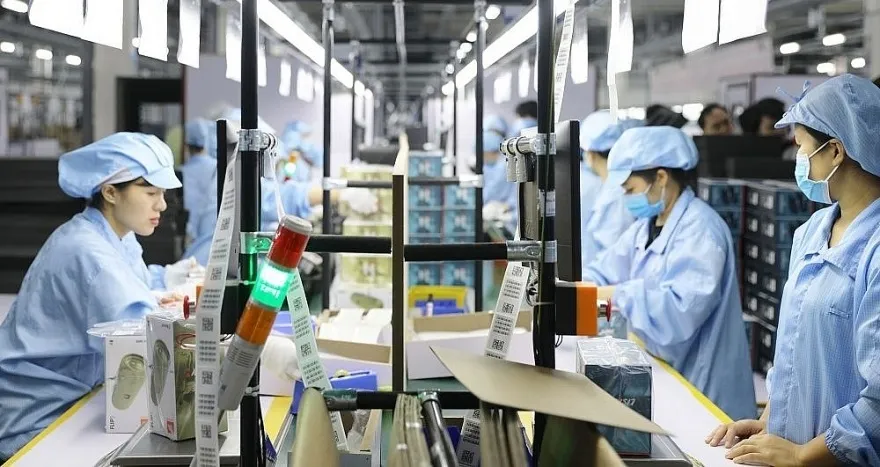
One of the foremost objectives is to achieve a GDP growth rate of 6-6.5%. This is an ambitious target, given the context of global and domestic economic challenges, difficulties, and uncertainties. However, the driving forces behind economic growth have shown improvement in recent times.
Forecasts for Economic Prospects
In 2023, the Vietnamese economy faced a challenging period, with the GDP growth target estimated at 5%, significantly lower than the National Assembly's initial target of 6-6.5% at the beginning of the year. By the end of November, the National Assembly passed a resolution on the economic and social development plan for 2024. Accordingly, the National Assembly continues to set a GDP growth target of 6-6.5% for the year 2024. Given the ongoing global uncertainties and the lack of signs of resolution in 2024, achieving this target is considered highly challenging. Some opinions even suggest that 2024 might be the second consecutive year where the GDP growth target cannot be met.
Nevertheless, reputable economic research organizations, both domestic and international, have provided varying forecasts for the growth prospects of the Vietnamese economy in 2024. For example, HSBC evaluates that Vietnam has successfully navigated through the most challenging phase, laying the groundwork for recovery in 2025, with a forecasted GDP growth rate of 6.3% in 2024. Similarly, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) predicts that Vietnam's GDP will increase by approximately 6% in 2024. Particularly optimistic, VinaCapital forecasts a growth rate of 6.5% in 2024, attributing it to the recovery of exports and manufacturing sectors.
On the other hand, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) presents a more cautious forecast with a growth rate of around 5.8%, placing Vietnam among the top 20 economies with the highest growth globally. The IMF believes that in 2023, Vietnam faced challenges in areas such as exports, real estate, and finance but is experiencing recovery. Especially, with the implementation of reform measures, Vietnam is expected to overcome "short-term headwinds" and sustain growth momentum in the medium term, based on integration into value chains and foreign direct investment (FDI).
The World Bank (WB) offers a more conservative outlook, predicting an economic growth of around 5.4% for Vietnam in 2024, increasing to 6% in 2025. Most recently, on December 13, in the Asia Development Outlook (ADO) report published by the Asian Development Bank (ADB), the growth forecast for Vietnam in 2024 was raised to 6%.
Expectations for Three Growth Drivers
In reality, the GDP growth target set by the National Assembly for 2024 is a significant challenge, but it remains achievable. According to Mr. Tran Van Lam, Standing Member of the Financial and Budgetary Committee of the National Assembly, Vietnam's GDP in 2024 could surpass 6%, achieving many of the goals set by the National Assembly. "Most economic recovery support packages were implemented in 2022 and the early months of 2023. These support packages need time to 'absorb,' and the effectiveness is expected to be realized in the late months of 2023 and onwards," Mr. Lam stated.
Meanwhile, many experts place their expectations on three primary growth drivers that show signs of acceleration in late 2023. Firstly, there is momentum in investment, encompassing both public and foreign investment, which is currently progressing rapidly. Specifically, in 2024, a series of major transportation infrastructure projects will officially commence, potentially boosting economic growth. Investment in infrastructure provides essential conditions to support production activities, cargo transportation, and services, while also attracting private investment and fostering business development. Collaborations in economic cooperation with South Korea, enhanced diplomatic relations with the United States and Japan, serve as drivers to stimulate new foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows into Vietnam, particularly in high-tech, semiconductor, and renewable energy sectors.
Next, the total retail sales of goods and services within the country have shown improvement in 2023. Overall, in the first 11 months of 2023, the total retail sales of goods and services at current prices reached an estimated VND 5,667,000 billion, a 9.6% increase compared to the same period last year. This improvement is further amplified by support policies, as in the recent session, the National Assembly agreed to reduce VAT from 10% to 8% for the first six months of 2024, with expectations of boosting domestic consumption. Assessing this policy, Associate Professor Dr. Tran Dinh Thien mentioned that in the early months of the year, retail sales grew by 15-17%, but in recent times, it has only increased by 11-12%, indicating a weakening momentum if this is considered a driving force. Therefore, effective solutions are needed to stimulate faster growth.
Finally, the economic growth momentum in 2024 is expected to come from import-export activities, as the advantages of new-generation free trade agreements (FTAs) begin to take effect. Thanks to certain tax incentives for exports, many of Vietnam's competitive goods can easily find new export partners. Evidence shows that in 2023, agricultural and aquatic products, especially vegetables, fruits, have benefited significantly from these FTAs. This is the only group of goods that recorded positive growth in the first 11 months of 2023, with export turnover estimated at USD 29.5 billion, an 8.6% increase. Some agricultural products witnessed impressive growth, such as the export turnover of fruits and vegetables reaching USD 5.32 billion, the highest increase at 74.5%; rice reaching USD 4.41 billion, a 36.3% increase (quantity increased by 16.2%); cashew nuts reaching USD 331 billion, a 17.4% increase (quantity increased by 23.1%)...
According to the assessments of many experts, amidst Vietnam's open economy and the increasing pace of export and import activities, to support and maximize profits from trade, reducing the trade deficit in transportation services, the government needs to issue preferential policies, remove difficulties, and address issues regarding mechanisms and funds to develop the container shipping fleet, especially container shipping fleets.